On Tesla AI Day 2022, Elon Musk revealed a working prototype of the Optimus Robotic. Nonetheless in early phases of improvement, Optimus works on the mechanism of Tesla’s self-driving vehicles and likewise showcases capabilities of sensible duties.
Although Optimus is skilled with methods like locomotion planning and utilizing sensors to foretell the strolling floor, Christian Hubicki, robotics professor and Director of Optimum Robotics Lab, identified that Optimus appears to be engaged on the tactic referred to as Zero-Second Level (ZMP) to stability its weight throughout every subsequent step by bending knees and tilting backwards or ahead.
ZMP is the dynamic mannequin for the management of legged locomotion (biped locomotion) in robots and humanoids. Primarily, the algorithm or method specifies the purpose the place the sum of gravity forces and horizontal inertia is zero throughout the contact of every foot to the bottom. This ensures that there is no such thing as a second of inertia within the horizontal path whereas strolling—which means, the robotic gained’t tip over whereas taking every step attributable to uneven weight distribution by guaranteeing all the burden is on the centre of gravity of the robotic.
Optimus makes use of electrical actuators for locomotion whereas the much-compared Boston Dynamics’ ATLAS makes use of a excessive powered hydraulic actuator which closely drains the battery. ‘Cassie’, the prototype bipedal robotic developed by Agility Robotics, balances itself dynamically at each step based mostly on the gait library technique and is a more in-depth comparability to the locomotion strategy of Tesla’s robotic’s Zero-Second Level (ZMP).
Biped locomotion has been researched for many years now. Miomir Vukobratović launched the idea of ZMP within the legged locomotion group in 1968 on the Third All-Union Congress of Theoretical and Utilized Mechanics in Moscow.
Biped Locomotion Mechanism
Biped robots are designed to imitate human-like locomotion and have a bonus over different multi-legged robots as a result of they’re extremely adaptable. No matter the construction and design of a robotic, the fundamental traits of a biped locomotion robotic are:
- Passive Levels of Freedom (DOF): DOF may be merely known as the variety of movable joints of a robotic. A passive DOF is the potential for incidence of a brand new “joint” due to disturbances from outdoors throughout motion of 1 foot, inflicting modifications within the total system.
- Gait repeatability or gait symmetry.
- Common interchangeability between double help part (DSP) and single help part (SSP).
The event and enchancment of biped robots and establishing these traits for stability has been challenged by few issues:
- Passive joints that aren’t in touch with the bottom make the constructions unstable.
- The gait cycle has various configurations throughout locomotion, altering with each step—DSP is when each toes are on the bottom and SSP is when one foot is on the bottom and the opposite is within the means of being transferred from again to entrance, also referred to as the ‘unstable’ stage.
- Robots work together with totally different surfaces and environments which impacts the algorithm.
ZMP in Optimus
In DSP, it’s straightforward to find out the zero-moment level by calculating the place of the centre of gravity (COG) or the hip trajectory. To keep up the steadiness of robots throughout SSP, which includes 80% of the gait cycle of a biped robotic, DSP is integrated and all of the joints are actuated and rigidly managed to trace the hip trajectory, which simplifies the management activity. Each of those processes rely upon linear pendulum mode (LPM) for prediction of the centre of gravity.
Since, the purpose of contact between the foot and the bottom can’t be managed straight like the opposite mechanism joints, it’s not directly managed by enabling and guaranteeing applicable dynamics of mechanism current above the foot, just like the COG of the hip trajectory. Subsequently, ZMP is the purpose the place all of the forces appearing on the mechanism may be changed by a single drive and must be contained in the help polygon.
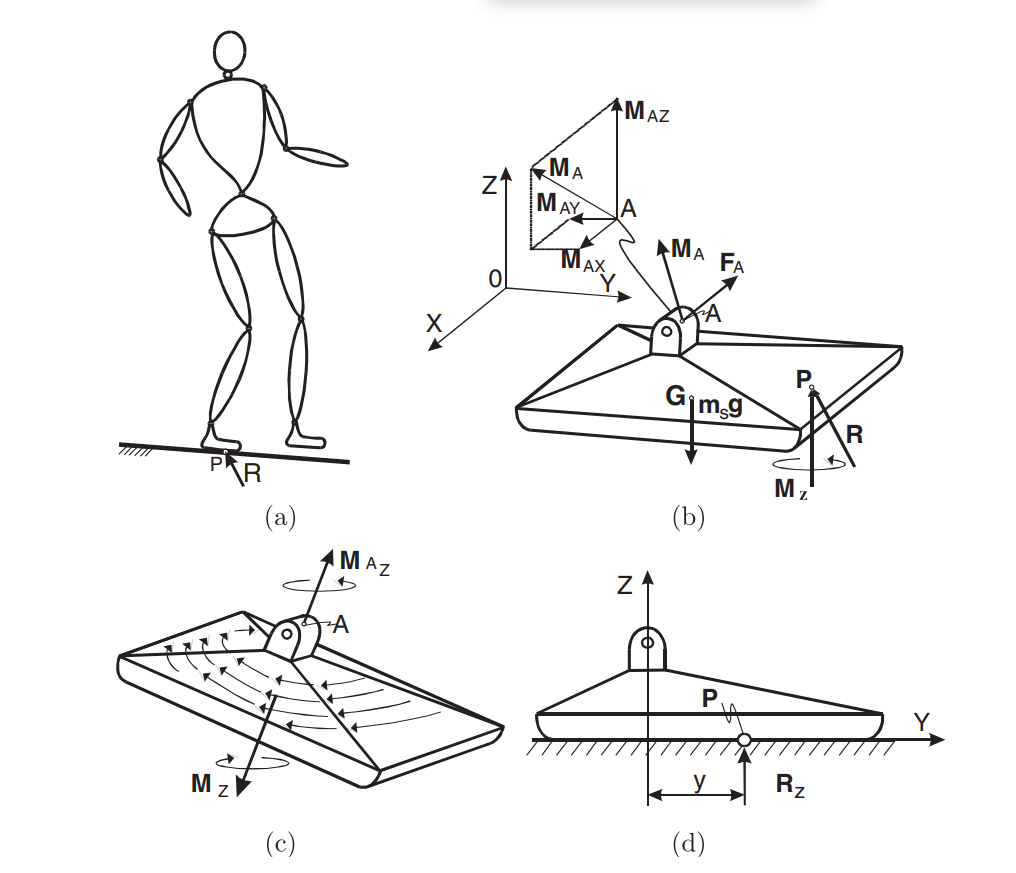
The help polygon is the realm on a horizontal aircraft the place the utilized and reactionary drive coincide, or just, the only real of the foot. In a balanced gait, ZMP and COG coincide, subsequently it’s straightforward to seek out out and preserve equilibrium within the mechanism. Within the above determine, ‘P’ is the zero-moment level.
Within the case of a disturbance that may trigger rotation of the foot, the ZMP would possibly shift to the sting of the foot and end in a disbalance of the mechanism. Although it nonetheless stays within the help polygon, the realm on the sting reduces, and thus causes imbalance. On this case, by monitoring the hip trajectory, the robotic can stability itself by shifting its weight throughout the system.
Subsequently, assumably, by coaching, locomotion planning, and scanning the strolling path and floor in entrance of it, the steps that Optimus takes by calculating the hip trajectory and bending its knees to make sure all of the drive is on its centre of gravity, appears to be engaged on a technique based mostly on Zero-Second Level calculation.


