
Cascading Style Sheets fondly known as CSS, is a merely designed language meant to simplify the method of constructing internet pages presentable. CSS means that you can apply types to internet pages. Extra importantly, CSS allows you to do that unbiased of the HTML that makes up every internet web page.
CSS is straightforward to be taught and understood, nevertheless it gives highly effective management over the presentation of an HTML doc.
We use CSS due to the next causes:
- CSS saves time: You may write CSS as soon as and reuse the identical sheet on a number of HTML pages.
- Simple Upkeep: To make a worldwide change merely change the fashion, and all parts in all of the webpages can be up to date mechanically.
- Search Engines: CSS is taken into account a clear coding approach, which implies search engines like google and yahoo gained’t need to wrestle to “learn” its content material.
- Superior types to HTML: CSS has a a lot wider array of attributes than HTML, so that you may give a much better look to your HTML web page compared to HTML attributes.
- Offline Shopping: CSS can retailer internet functions domestically with the assistance of an offline cache. Utilizing of this we are able to view offline web sites.
3. What are the benefits of CSS?
- CSS performs an essential function, through the use of CSS you merely bought to specify a repeated fashion for a component as soon as & use it a number of instances as a result of CSS will mechanically apply the required types.
- The principle benefit of CSS is that fashion is utilized persistently throughout quite a lot of websites. One instruction can management a number of areas that are advantageous.
- Net designers want to make use of a number of traces of programming for each web page enhancing web site velocity.
- Cascading sheet not solely simplifies web site growth but additionally simplifies upkeep as a change of 1 line of code impacts the entire web site and upkeep time.
- It’s much less complicated subsequently the trouble is considerably lowered.
- It helps to type spontaneous and constant adjustments.
- CSS adjustments are machine pleasant. With folks using a batch of varied vary of sensible units to entry web sites over the net, there’s a requirement for responsive internet design.
- It has the ability for re-positioning. It helps us to find out the adjustments inside the place of internet parts which are there on the web page.
- These bandwidth financial savings are substantial figures of insignificant tags which are vague from a multitude of pages.
- Simple for the consumer to customise the net web page
- It reduces the file switch measurement.
4. What are the disadvantages of CSS?
- CSS, CSS 1 as much as CSS3, end in creating confusion amongst internet browsers.
- With CSS, what works with one browser may not all the time work with one other. The online builders want to check for compatibility, operating this system throughout a number of browsers.
- There exists a shortage of safety.
- After making the adjustments we have to affirm the compatibility if they seem. An identical change impacts all of the browsers.
- The programing language world is difficult for non-developers and rookies. Totally different ranges of CSS i.e. CSS, CSS 2, CSS 3 are sometimes fairly complicated.
- Browser compatibility (some fashion sheets are supported and a few should not).
- CSS works in another way on completely different browsers. IE and Opera assist CSS as completely different logic.
- There is perhaps cross-browser points whereas utilizing CSS.
- There are a number of ranges that create confusion for non-developers and rookies.
5. What’s the present model of CSS?
CSS3 is the most recent model of CSS
6. How is CSS completely different from CSS 3?
|
S.No. |
CSS |
CSS3 |
| 1 | CSS is able to positioning texts and objects. CSS is in some way backward suitable with CSS3. | Then again, CSS3 is able to making the net web page extra engaging and takes much less time to create. When you write CSS3 code in CSS, will probably be invalid. |
| 2 | Responsive designing shouldn’t be supported in CSS | CSS3 is the most recent model, therefore it helps responsive design. |
| 3 | CSS can’t be break up into modules. | Whereas, whereas CSS3 may be breakdown into modules. |
| 4 | Utilizing CSS, we can’t construct 3D animation and transformation. | However in CSS3 we are able to carry out all types of animation and transformations because it helps animation and 3D transformations. |
| 5 | CSS may be very sluggish as in comparison with CSS3 | Whereas, CSS3 is quicker than CSS. |
7. Checklist the CSS Frameworks.
The perfect CSS frameworks are:
- Bootstrap
- Basis
- Bulma
- UIKit
- Semantic UI
- Materialize
- Pure
- Tailwind CSS
A CSS fashion rule consists of a selector, property, and its worth. The selector factors to the HTML aspect the place CSS fashion is to be utilized. The CSS property is separated by semicolons.
Syntax:
selector {
Property: worth;
}
9. In what number of methods can we add CSS to our HTML file?
Cascading Type Sheet(CSS) is used to set the fashion in internet pages that include HTML parts. It units the background shade, font measurement, font household, shade, … and so forth properties of parts on an internet web page.
There are three sorts of CSS that are given under:
- Inline CSS: Inline CSS comprises the CSS property within the physique part hooked up with the aspect often called inline CSS. This sort of fashion is specified inside an HTML tag utilizing the fashion attribute.
- Inner or Embedded CSS: This can be utilized when a single HTML doc have to be styled uniquely. The CSS ruleset needs to be inside the HTML file within the head part i.e the CSS is embedded inside the HTML file.
- Exterior CSS: Exterior CSS comprises a separate CSS file which comprises solely fashion property with the assistance of tag attributes (For instance class, id, heading, … and so forth). CSS property is written in a separate file with .css extension and needs to be linked to the HTML doc utilizing the hyperlink tag. Which means that for every aspect, fashion may be set solely as soon as and that can be utilized throughout internet pages.
10. Which sort of CSS holds the very best precedence?
Inline CSS has the very best precedence, then comes Inner/Embedded adopted by Exterior CSS which has the least precedence. A number of fashion sheets may be outlined on one web page. If for an HTML tag, types are outlined in a number of fashion sheets then the under order can be adopted.
- As Inline has the very best precedence, any types which are outlined within the inner and exterior fashion sheets are overridden by Inline types.
- Inner or Embedded stands second within the precedence record and overrides the types within the exterior fashion sheet.
- Exterior fashion sheets have the least precedence. If there aren’t any types outlined both within the inline or inner fashion sheet then exterior fashion sheet guidelines are utilized for the HTML tags.
CSS Selectors: CSS Selectors are used to deciding on HTML parts based mostly on their aspect title, id, attributes, and so forth. It could choose a number of parts concurrently.
aspect selector: The aspect selector in CSS is used to pick HTML parts that are required to be styled. In a selector declaration, there may be the title of the HTML aspect, and the CSS properties that are to be utilized to that aspect is written contained in the brackets {}.
Syntax:
element_name {
// CSS Property
}
id selector: The #id selector is used to set the fashion of the given id. The id attribute is the distinctive identifier in an HTML doc. The id selector is used with a # character.
Syntax:
#id_name {
// CSS Property
}
class selector: The .class selector is used to pick all parts which belong to a selected class attribute. To pick the weather with a selected class, use the (.) character with specifying the category title. The category title is generally used to set the CSS property to the given class.
Syntax:
.class_name {
// CSS Property
}
12. How can we add feedback in CSS?
Feedback are the statements in your code which are ignored by the compiler and should not executed. Feedback are used to clarify the code. They make this system extra readable and comprehensible.
Syntax:
/* content material */
Feedback may be single-line or multi-line.
13. What does the ‘a’ in rgba imply?
RGBA comprises A (Alpha) which specifies the transparency of parts. The worth of alpha lies between 0.0 to 1.0 the place 0.0. represents absolutely clear and 1.0 represents not clear.
Syntax:
h1 {
shade:rgba(R, G, B, A);
}
14. What are CSS HSL Colours?
HSL: HSL stands for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness respectively. This format makes use of the cylindrical coordinate system.
- Hue: Hue is the diploma of the colour wheel. Its worth lies between 0 to 360 the place 0 represents purple, 120 represents inexperienced and 240 represents a blue shade.
- Saturation: It takes a proportion worth, the place 100% represents fully saturated, whereas 0% represents fully unsaturated (grey).
- Lightness: It takes a proportion worth, the place 100% represents white, whereas 0% represents black.
Syntax:
h1 {
shade:hsl(H, S, L);
}
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

15. What are CSS backgrounds, record the properties?
The CSS background properties are used to outline the background results for parts.
CSS background properties are as follows :
- background-color: This property specifies the background shade of a component.
- background-image: This property specifies a picture to make use of because the background of a component. By default, the picture is repeated so it covers all the aspect.
- background-repeat: By default, the background picture property repeats the picture each horizontally and vertically.
- background-attachment: This property is used to repair the background floor picture. The picture won’t scroll with the web page.
- background-position: This property is used to set the picture to a selected place.
16. What are the completely different CSS border properties?
CSS border properties enable us to set the fashion, shade, and width of the border.
- Border Type: The border-style property specifies the kind of border. Not one of the different border properties will work with out setting the border fashion.
- Border Width: Border width units the width of the border. The width of the border may be in px, pt, cm or skinny, medium and thick.
- Border Coloration: This property is used to set the colour of the border. Coloration may be set utilizing the colour title, hex worth, or RGB worth. If the colour shouldn’t be specified border inherits the colour of the aspect itself.
17. What does margin: 40px 100px 120px 80px signify?
CSS margins are used to create house across the aspect. We are able to set the completely different sizes of margins for particular person sides (prime, proper, backside, left).
Margin properties can have the next values:
- Size in cm, px, pt, and so forth.
- Width % of the aspect.
- Margin calculated by the browser: auto.
Due to this fact, margin: 40px 100px 120px 80px signifies:
- prime = 40px
- proper = 100px
- backside = 120px
- left = 80px
18. What’s the distinction between margin and padding?
- Margin is used to create house round parts and padding is used to create house round parts contained in the border.
- We are able to set the margin property to auto however we can’t set the padding property to auto.
- In Margin property we are able to enable unfavorable or float quantity however in padding we can’t enable unfavorable values.
- Margin and padding goal all of the 4 sides of the aspect. Margin and padding will work with out the border property additionally. The distinction can be extra clear with the next instance.
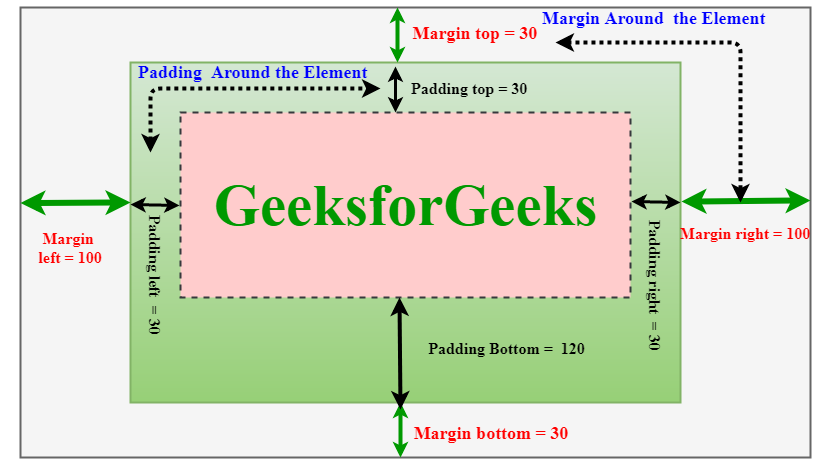
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

19. What’s CSS Field Mannequin?
The CSS field mannequin is a container that comprises a number of properties together with borders, margin, padding, and the content material itself. It’s used to create the design and structure of internet pages. It may be used as a toolkit for customizing the structure of various parts. The online browser renders each aspect as an oblong field in keeping with the CSS field mannequin.
Field-Mannequin has a number of properties in CSS. A few of them are given under:
- borders
- margins
- padding
- Content material
The next determine illustrates the field mannequin.
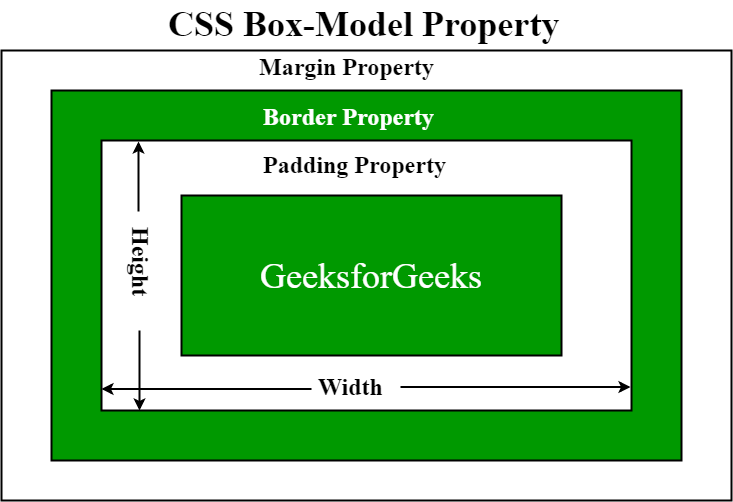
- Border Space: It’s the space between the field’s padding and margin. Its dimensions are given by the width and peak of the border.
- Margin Space: This space consists of house between border and margin. The scale of the Margin space are the margin-box width and the margin-box peak. It’s helpful to separate the aspect from its neighbors.
- Padding Space: It consists of the aspect’s padding. This space is definitely the house across the content material space and inside the border field. Its dimensions are given by the width of the padding-box and the peak of the padding-box.
- Content material Space: This space consists of content material like textual content, photographs, or different media content material. It’s bounded by the content material edge and its dimensions are given by content material field width and peak.
20. What’s the distinction between CSS border and description?
- CSS border properties enable us to set the fashion, shade, and width of the border.
- CSS define property permits us to attract a line across the aspect, exterior the border.
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:
Variations:
- In contrast to borders, outlines don’t enable us to set every edge to a unique width, or set completely different colours and types for every edge. A top level view is identical on all sides.
- Outlines can’t be round.
- Outlines don’t take up house, as a result of they’re all the time positioned on prime of the field of the aspect.
21. How can we format textual content in CSS?
CSS textual content formatting properties are used to format textual content and elegance textual content.
CSS textual content formatting consists of the next properties:
- Textual content-color
- Textual content-alignment
- Textual content-decoration
- Textual content-transformation
- Textual content-indentation
- Letter spacing
- Line peak
- Textual content-direction
- Textual content-shadow
- Phrase spacing
22. What are the completely different CSS hyperlink states?
A hyperlink is a connection from one internet web page to a different internet web page. CSS property can be utilized to fashion the hyperlinks in numerous other ways.
States of Hyperlink: Earlier than discussing CSS properties, it is very important know the states of a hyperlink. Hyperlinks can exist in several states and they are often styled utilizing pseudo-classes.
There are 4 states of hyperlinks given under:
- a:hyperlink: This can be a regular, unvisited hyperlink.
- a:visited: This can be a hyperlink visited by a consumer at the very least as soon as
- a:hover: This can be a hyperlink when the mouse hovers over it
- a:energetic: This can be a hyperlink that’s simply clicked.
23. Can we add a picture as an inventory merchandise marker?
So as to add a picture because the list-item marker in an inventory, we use the list-style-image property in CSS.
Syntax:
list-style-image: none | url | preliminary | inherit;
24. How can we conceal a component in CSS?
The fashion show property is used to cover and present the content material of HTML DOM by accessing the DOM aspect utilizing JavaScript/jQuery.
To cover a component, set the fashion show property to “none”.
show: "none";
To point out a component, set the fashion show property to “block”.
show:"block";
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:
The visibility property is used to cover or present the content material of HTML parts. The visibility property specifies that the aspect is presently seen on the web page. The ‘hidden’ worth can be utilized to cover the aspect. This hides the aspect however doesn’t take away the house taken by the aspect, in contrast to the show property.
Syntax:
visibility : 'hidden'; visibility :'seen';
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:
25. What’s the distinction between show: none and visibility: hidden?
Each of the property is sort of helpful in CSS. The visibility: “hidden”; property is used to specify whether or not a component is seen or not in an internet doc however the hidden parts take up house within the internet doc. The visibility is a property in CSS that specifies the visibility habits of a component and show: “none” property is used to specify whether or not a component is exist or not on the web site.
Syntax:
visibility: seen| hidden | collapse | preliminary | inherit;
show: none | inline | block | inline-block;
So, the distinction between show: “none”; and visibility: “hidden”;, proper from the title itself we are able to inform the distinction as show: “none”, fully will get rids of the tag, because it had by no means existed within the HTML web page whereas visibility: “hidden”;, simply makes the tag invisible it would nonetheless be on the HTML web page occupying house it’s simply invisible.
26. Can we overlap parts in CSS?
Creating an overlay impact merely means placing two div collectively on the similar place however each the div seem when wanted i.e whereas hovering or whereas clicking on one of many div to make the second seem. Overlays are very clear and provides the webpage a tidy look. It appears to be like refined and is straightforward to design. Overlays can create utilizing two easy CSS properties:
The z-index property is used to displace parts on the z-axis i.e in or out of the display. It’s used to outline the order of parts in the event that they overlap with one another.
Syntax:
z-index: auto|quantity|preliminary|inherit;
The place property in CSS tells concerning the methodology of positioning for a component or an HTML entity.
27. What are the assorted positioning properties in CSS?
The place property in CSS tells concerning the methodology of positioning for a component or an HTML entity. There are 5 several types of place properties obtainable in CSS:
- Fastened
- Static
- Relative
- Absolute
- Sticky
The positioning of a component may be completed utilizing the prime, proper, backside, and left properties. These specify the space of an HTML aspect from the sting of the viewport. To set the place by these 4 properties, we have now to declare the positioning methodology.
Let’s speak about every of those place strategies intimately:
1. Fastened: Any HTML aspect with place: mounted property can be positioned relative to the viewport. A component with mounted positioning permits it to stay on the similar place whilst we scroll the web page. We are able to set the place of the aspect utilizing the highest, proper, backside, and left.
2. Static: This methodology of positioning is about by default. If we don’t point out the strategy of positioning for any aspect, the aspect has the place: static methodology by default. By defining Static, the highest, proper, backside and left won’t have any management over the aspect. The aspect can be positioned with the traditional circulation of the web page.
3. Relative: A component with place: relative is positioned comparatively with the opposite parts that are sitting at prime of it. If we set its prime, proper, backside, or left, different parts won’t replenish the hole left by this aspect.
4. Absolute: A component with place: absolute can be positioned with respect to its mum or dad. The positioning of this aspect doesn’t depend on its siblings or the weather that are on the similar stage.
5. Sticky: Ingredient with place: sticky and prime: 0 performed a job between mounted & relative based mostly on the place the place it’s positioned. If the aspect is positioned in the course of the doc then when the consumer scrolls the doc, the sticky aspect begins scrolling till it touches the highest. When it touches the highest, will probably be mounted at that place regardless of additional scrolling. We are able to stick the aspect on the backside, with the backside property.
The CSS overflow controls the large content material. It tells whether or not to clip content material or so as to add scroll bars. The overflow comprises the next property:
1. Seen: The content material shouldn’t be clipped and is seen exterior the aspect field.
2. Hidden: The overflow is clipped and the remainder of the content material is invisible.
3. Scroll: The overflow is clipped however a scrollbar is added to see the remainder of the content material. The scrollbar may be horizontal or vertical.
4. Auto: It mechanically provides a scrollbar every time it’s required.
Overflow-x and Overflow-y: This property specifies how you can change the overflow of parts. x offers with horizontal edges and y offers with vertical edges.
29. What does the CSS float property do?
Float is a CSS property written in a CSS file or instantly within the fashion of a component. The float property defines the circulation of content material. Under are the sorts of floating properties:
| Float sort | Utilization |
|---|---|
| float: left | Ingredient floats on the left aspect of the container |
| float: proper | Ingredient floats on the correct aspect of the container |
| float: inherit | The aspect inherits the floating property of its mum or dad (div, desk, and so forth…) |
| float: none | Ingredient is displayed as it’s (Default). |
30. What does show:inline-block do?
Inline-block: This function makes use of each properties: block and inline. So, this property aligns the div inline however the distinction is it may well edit the peak and the width of the block. Principally, this may align the div each within the block and inline style.
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

31. How can we vertically middle a textual content in CSS?
This resolution will work for a single line and a number of traces of textual content, nevertheless it nonetheless requires a set peak container:
div {
peak: 200px;
line-height: 200px;
text-align: middle;
border: 2px dashed #f69c55;
}
span {
show: inline-block;
vertical-align: center;
line-height: regular;
}
div{
GeeksforGeeks
}

32. How can we middle a picture in CSS?
Given a picture and the duty is to set the picture to align to middle (vertically and horizontally) inside a much bigger div. It may be completed through the use of the place property of the aspect.
Instance: This instance makes use of the place property to make the picture align to the middle.
HTML
|
|
Output:

CSS combinators are explaining the connection between two selectors. CSS selectors are the patterns used to pick the weather for fashion functions. A CSS selector could be a easy selector or a posh selector consisting of a couple of selector related utilizing combinators.
There are 4 sorts of combinators obtainable in CSS that are mentioned under:
- Common Sibling selector (~)
- Adjoining Sibling selector (+)
- Little one selector (>)
- Descendant selector (house)
Common Sibling selector: The final sibling selector is used to pick the aspect that follows the primary selector aspect and in addition shares the identical mum or dad as the primary selector aspect. This can be utilized to pick a gaggle of parts that share the identical mum or dad aspect.
Adjoining Sibling selector: The Adjoining sibling selector is used to pick the aspect that’s adjoining or the aspect that’s subsequent to the desired selector tag. This combinator selects just one tag that’s simply subsequent to the desired tag.
Little one Selector: This selector is used to pick the aspect that’s the rapid little one of the desired tag. This combinator is stricter than the descendant selector as a result of it selects solely the second selector if it has the primary selector aspect as its mum or dad.
Descendant selector: This selector is used to pick all of the little one parts of the desired tag. The tags may be the direct little one of the desired tag or may be very deep within the specified tag. This combinator combines the 2 selectors such that chosen parts have an ancestor similar as the primary selector aspect.
34. What are pseudo-classes in CSS?
A Pseudo class in CSS is used to outline the particular state of a component. It may be mixed with a CSS selector so as to add an impact to current parts based mostly on their states. For Instance, altering the fashion of a component when the consumer hovers over it, or when a hyperlink is visited. All of those may be completed utilizing Pseudo Courses in CSS.
Observe that pseudo-class names should not case-sensitive.
Syntax:
selector: pseudo-class{
property: worth;
}
There are numerous Pseudo-classes in CSS however the ones that are mostly used are as follows:
- :hover Pseudo-class: This pseudo-class is used so as to add a particular impact to a component when our mouse pointer is over it. The under instance demonstrates that when your mouse enters the field space, its background shade adjustments from yellow to orange.
- :energetic Pseudo-class: This pseudo-class is used to pick a component that’s activated when the consumer clicks on it. The next instance demonstrates that whenever you click on on the field, its background shade adjustments for a second.
- :focus Pseudo-class: This pseudo-class is used to pick a component that’s presently focussed by the consumer. It really works on consumer enter parts utilized in varieties and is triggered as quickly because the consumer clicks on it. Within the following instance, the background shade of the enter discipline which is presently centered adjustments.
- :visited Pseudo-class: This pseudo-class is used to pick the hyperlinks which have been already visited by the consumer. Within the following instance, the colour of the hyperlink adjustments as soon as it’s visited.
35. What are pseudo-elements in CSS?
Pseudo Parts: Pseudo-element in CSS is used so as to add fashion to specified elements of a component. Instance: Utilizing fashion earlier than or after a component.
Syntax:
selector::pseudo-element {
property:worth;
}
Use of Pseudo-Ingredient: Under is a few examples to explain using pseudo-element.
- ::earlier than Pseudo-element: It’s used so as to add some CSS property earlier than a component when that aspect is named.
- ::after Pseudo-element: It’s used so as to add some CSS property after a component when that aspect is named.
- ::first-letter Pseudo-element: It’s used to make adjustments to the primary letter of a component.
- ::first-line Pseudo-element: It’s used to make adjustments to the primary line of a component.
36. How can we add gradients in CSS?
There are two sorts of Gradients:
1. Linear Gradients: It consists of the graceful shade transitions to going up, down, left, proper, and diagonally. A minimal of two colours are required to create a linear gradient. Greater than two shade parts may be attainable in linear gradients. The place to begin and the course are wanted for the gradient impact.
Syntax:
background-image: linear-gradient(course, color-stop1, color-stop2, ...);
2. CSS Radial Gradients: A radial gradient differs from a linear gradient. It begins at a single level and emanates outward. By default, the primary shade begins on the middle place of the aspect after which fades to the tip shade in the direction of the sting of the aspect. Fade occurs at an equal charge till specified.
Syntax:
background-image: radial-gradient(form measurement at place, start-color, ..., l
37. Can we add 2D transformations to our challenge utilizing CSS?
Sure, we are able to, a metamorphosis modifies a component by its form, measurement, and place. It transforms the weather alongside the X-axis and Y-axis.
There are six essential sorts of 2D transformations that are listed under:
- translate()
- rotate()
- scale()
- skewX()
- skewY()
- matrix()
38. Can we add 3D transformations to our challenge utilizing CSS?
Sure, it permits altering parts utilizing 3D transformations. In 3D transformation, the weather are rotated alongside the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis.
There are three essential sorts of transformation that are listed under:
- rotateX()
- rotateY()
- rotateZ()
Transitions in CSS enable us to manage the best way by which transition takes place between the 2 states of the aspect.
The transition permits us to find out how the change in shade takes place. We are able to use the transitions to animate the adjustments and make the adjustments visually interesting to the consumer and therefore, giving a greater consumer expertise and interactivity. On this article, we’ll present you how you can animate the transition between the CSS properties.
There are 4 CSS properties that it’s best to use, all or partially (at the very least two, transition-property and transition-duration, is a should), to animate the transition. All these properties have to be positioned together with different CSS properties of the preliminary state of the aspect:
- transition-property: This property means that you can choose the CSS properties which you wish to animate throughout the transition(change).
Syntax:
transition-property: none | all | property | property1, property2, ..., propertyN;
- transition-duration: This property means that you can decide how lengthy it would take to finish the transition from one CSS property to the opposite.
Syntax:
transition-duration: time;
Right here, time may be in seconds(s) or milliseconds(ms), it’s best to use ‘s’ or ‘ms’ after the quantity (with out quotes).
- transition-timing-function: This property means that you can decide the velocity of change and the way of change, throughout the transition. Like, the change needs to be quick firstly and sluggish on the finish, and so forth.
Syntax:
transition-timing-function: ease|ease-in|ease-out|ease-in-out|linear| step-start|step-end;
- transition-delay: This property means that you can decide the period of time to attend earlier than the transition truly begins to happen.
Syntax:
transition-delay: time;
Right here, once more, time may be in seconds(s) or milliseconds(ms), and it’s best to use ‘s’ or ‘ms’ after the quantity (with out quotes).
- The Shorthand Property You may mix all of the 4 transition properties talked about above, into one single shorthand property, in keeping with the syntax given under. This protects us from writing lengthy codes and prevents us from getting messy. Observe the ordering of property, it has significance.
Syntax:
transition: (property title) | (length) | (timing perform) | (delay);
40. How can we animate utilizing CSS?
CSS Animations is a way to vary the looks and habits of varied parts in internet pages. It’s used to manage the weather by altering their motions or show. It has two elements, one which comprises the CSS properties which describe the animation of the weather and the opposite comprises sure keyframes which point out the animation properties of the aspect and the precise time intervals at which these need to happen.
The @keyframes rule: Keyframes are the foundations with the assistance of which CSS Animations works. They outline the show of the animation on the respective levels of its complete length. For instance: Within the following code, the paragraph adjustments its shade with time. At 0% completion, it’s purple, at 50% completion it’s of orange shade and at full completion i.e. at 100%, it’s brown.
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

41. What does the CSS box-sizing property do?
The box-sizing CSS property defines how the consumer ought to calculate the whole width and peak of a component i.e. padding and borders, are to be included or not.
Syntax:
box-sizing: content-box|border-box;
Property Values:
- content-box: That is the default worth of the box-sizing property. On this mode, the width and peak properties embrace solely the content material. Border and padding should not included in it i.e if we set a component’s width to 200 pixels, then the aspect’s content material field can be 200 pixels broad, and the width of any border or padding can be added to the ultimate rendered width.
- border-box: On this mode, the width and peak properties embrace content material, padding, and borders i.e if we set a component’s width to 200 pixels, that 200 pixels will embrace any border or padding we added, and the content material field will shrink to soak up that additional width. This sometimes makes it a lot simpler to measurement parts.
42. How can we make our web site responsive utilizing CSS?
Media question is used to create a responsive internet design. It signifies that the view of an internet web page differs from system to system based mostly on display or media varieties.
Media queries can be utilized to verify many issues:
- width and peak of the viewport
- width and peak of the machine
- Orientation
- Decision
A media question include a media sort that may include a number of expression which may be both true or false. The results of the question is true if the desired media matches the kind of machine the doc is displayed on. If the media question is true then a method sheet is utilized.
Syntax:
@media not | solely mediatype and (expression) {
// Code content material
}
Additionally it is referred to as a versatile field mannequin. It’s principally a structure mannequin that gives a straightforward and clear solution to prepare objects inside a container. Flexbox is completely different from the block mannequin which is vertically biased and the inline which is horizontally biased. Flexbox was created for small-scale layouts and there’s one other customary referred to as grids that are geared extra in the direction of larger-scale layouts, It really works just like the best way to Twitter bootstrap grid system works. Flexbox is responsive and mobile-friendly. To start out with flexbox firstly create a flex container. To create a flex container set the show property to flex.
Syntax:
.main-container {
show: flex;
}
Flex Properties:
- flex-direction
- flex-wrap
- flex-flow
- justify-content
- align-items
- align-content
It’s a CSS property that provides a grid-based structure system, with rows and columns, making it simpler to design internet pages with out floats and positioning.

Syntax:
grid: none|grid-template-rows / grid-template-columns|grid-template-areas| grid-template-rows / [grid-auto-flow] grid-auto-columns|[grid-auto-flow] grid-auto-rows / grid-template-columns|preliminary|inherit;
45. What’s the distinction between flexbox and grid?
1. Dimensionality and Flexibility:
- Flexbox gives better management over alignment and house distribution between objects. Being one-dimensional, Flexbox solely offers with both columns or rows.
- The grid has two-dimension structure capabilities which permit versatile widths as a unit of size. This compensates for the restrictions in Flex.
2. Alignment:
- Flex Path permits builders to align parts vertically or horizontally, which is used when builders create and reverse rows or columns.
- CSS Grid deploys fractional measure models for grid fluidity and auto-keyword performance to mechanically modify columns or rows.
3. Merchandise Administration
- Flex Container is the mum or dad aspect whereas Flex Merchandise represents the kids. The Flex Container can guarantee balanced illustration by adjusting merchandise dimensions. This enables builders to design for fluctuating display sizes.
- Grid helps each implicit and express content material placement. Its inbuilt automation permits it to mechanically lengthen line objects and replica values into the brand new creation from the previous merchandise.
|
Property |
Grid |
Flexbox |
|
Dimension |
Two – Dimensional |
One – Dimensional |
|
Options |
Can flex mixture of things by space-occupying Options |
Can push content material aspect to excessive alignment |
|
Assist Sort |
Format First |
Content material First |
46. What’s one of the best ways to incorporate a CSS file? Why use @import?
The Exterior Type Sheet (utilizing HTML <hyperlink> Tag) is one of the best methodology that’s used to hyperlink the aspect. Sustaining and re-using the CSS file throughout completely different pages is straightforward and environment friendly. The <hyperlink> tag is positioned within the HTML <head> aspect. To specify a media sort=”textual content/css” for a Cascading Type Sheet <sort> attribute which is used to disregard fashion sheet varieties that aren’t supported in a browser.
@import rule: The @import rule is used to import one fashion sheet into one other fashion sheet. This rule additionally helps media queries in order that the consumer can import the media-dependent fashion sheet. The @import rule have to be declared on the prime of the doc after any @charset declaration.
Traits of @import:
- The @import at-rule is used to import a method sheet into an HTML web page or one other fashion sheet.
- The @import at-rule can also be used so as to add media queries, subsequently import is media-dependent.
- It’s all the time to be declared on the prime of the doc.
Syntax:
@import url|string list-of-mediaqueries;
47. How case-sensitive is CSS?
All CSS fashion sheets are case-insensitive, apart from parts that aren’t beneath the management of CSS. For instance, the case sensitivity attributable to values of the HTML attributes “id” and “class”, font names, and URIs lies exterior the scope of this specification.
48. What does CSS Animations enable?
CSS permits the animation of HTML parts with out utilizing JavaScript. An animation lets a component systematically and with correct timing, change from one fashion to a different. You may change no matter CSS properties you need, and finish quite a lot of instances, as you need it. To make use of CSS animation, you should first specify some @keyframes for the animation. @keyframes will describe which types that aspect can have at particular instances. We can be utilizing a fundamental instance such because the animation of a battery charging.
The @keyframes property has the choice to divide the animation time into elements/proportion and carry out an exercise that’s specified for that a part of the entire length of the animation. The @keyframes property is given to every animation in keeping with the title of that animation. It means that you can run the animation infinitely as effectively.
49. What’s @keframes used for?
Keyframes are the foundations with the assistance of which CSS Animations works. They outline the show of the animation on the respective levels of its complete length. For instance: Within the following code, the paragraph adjustments its shade with time. At 0% completion, it’s purple, at 50% completion it’s of orange shade and at full completion i.e. at 100%, it’s brown.
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

Counters in CSS are principally variables that can be utilized for numbering and values of CSS counters could also be incremented by CSS guidelines. For instance, CSS counters can be utilized to increment the numbering of the headings mechanically. In HTML, the <ol> tag is used to provide the ordered numbers to record objects however CSS comprises a counter to provide order parts in another style.
CSS counters properties: CSS counters comprises the next properties:
- counter-reset: It’s used to reset a counter.
- counter-increment: It principally increments a counter worth.
- content material: It’s used to generate content material.
- counter() or counters() perform: The worth of a counter may be displayed utilizing both the counter() or counters() perform in a content material property. These two capabilities principally used so as to add the worth of a counter to the aspect.
Initialization of the CSS Counter: To make use of the CSS counter property firstly it have to be created with the counter-reset property and step one is resetting the counter. The counter by default initialized to a price 0(zero) with the counter-reset property.
Syntax:
counter-reset: myCounter;
Incrementation and Use of CSS Counter: To increment the counter use the CSS counter-increment property.
Syntax:
counter-increment: myCounter;
The counter() or counters() perform in content material is used to show the content material in a selected order.
Syntax:
content material: counter(myCounter);
51. What is supposed by common selector?
The * selector in CSS is used to pick all the weather in an HTML doc. It additionally selects all parts that are inside beneath one other aspect. Additionally it is referred to as the common selector.
Syntax:
* {
// CSS property
}
Responsive Net Design contains two phrases i.e., responsive and internet design. Responsive means to reply and internet design means to design an internet site. Due to this fact, responsive internet design usually means the web site that responds to or resizes or adjusts itself relying upon the display measurement it’s being seen by. It mechanically adjusts to suit the consumer’s display whether or not it’s desktop, laptop computer, cellular, pill, and so forth. It solely makes use of one structure for an internet web page and it may be completed both utilizing CSS and HTML or CSS3 and HTML5.
53. What’s the distinction between class and id selector?
Id selector(“#”): The id selector selects the id attribute of an HTML aspect to pick a particular aspect. An id is all the time distinctive inside the web page so it’s chosen to pick a single, distinctive aspect. It’s written with the hash character (#), adopted by the id of the aspect.
#element_id_name{
// CSS properties
}
Class Selector(“.”): The category selector selects HTML parts with a particular class attribute. It’s used with a interval character “.” (full cease image) adopted by the category title.
.element_class_name{
// CSS properties
}
Distinction between class (“.”) and id (“#”) Selectors:
|
Class “.” |
Id “#” |
| The category selector “.” is used to signify class=”class_name” in HTML aspect. | The id selector “#” is used to signify id=”id_name” in HTML aspect. |
| Every parts can include extra that one “.” selector signifies that parts is containing a couple of class which is separated by house, the can be chosen by a number of dots like .class1 .class2 …. and so forth. | Every aspect can include just one “#” selector, not a couple of in contrast to class selectors. |
| The “.” selectors should not distinctive, similar selectors can relevant on a number of parts, if the HTML parts holds the identical class property like an inventory of parts can comprises the identical class. |
54. How can we use pagination in CSS?
Pagination is the method of dividing the doc into pages and offering them with numbers.
Kinds of Pagination: There are numerous sorts of pagination in CSS. A few of them are given under:
- Easy Pagination
- Lively and Hoverable Pagination
- Rounded Lively and Hoverable Buttons
- Hoverable Transition Impact
- Bordered Pagination
- Rounded Border Pagination
- Centered Pagination
- Area between Pagination
- Pagination Measurement
Easy Pagination: That is the essential type of pagination.
Syntax:
.pagination {
show:sort
}
.pagination physique {
shade:colorname
ornament:sort
}
55. What’s CSS Picture reflection?
The box-reflect property is used to create a picture reflection.
Attributes:
- under: to create a mirrored image under the unique picture
- above: to create a mirrored image above the unique picture
- left: to create a mirrored image on the left aspect of the unique picture
- proper: to create a mirrored image on the correct aspect of the unique picture
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:
56. How can we create a number of columns of text-like newspapers utilizing CSS?
The a number of columns are used to create column layouts on the internet pages. There are numerous column properties in CSS that are listed under:
- column-count
- column-gap
- column-rule-style
- column-rule-width
- column-rule-color
- column-rule
- column-span
- column-width
Instance:
HTML
|
|
Output:

57. How can we give a shadow impact to our textual content in CSS?
The strategy of this text is so as to add a shadow utilizing the text-shadow property in CSS. This property accepts an inventory of a comma-separated record of shadows to be utilized to the textual content. The default worth of the text-shadow property is “none”.
Syntax:
text-shadow: h-shadow v-shadow blur-radius shade|none|preliminary|
The !essential property in CSS is used to supply extra weight (significance) than regular property. In CSS, the !essential signifies that “that is essential”, ignore all the next guidelines, and apply !essential rule and the !essential key phrase have to be positioned on the finish of the road, instantly earlier than the semicolon.
- In different phrases, it provides significance to all of the sub-properties that the shorthand property represents.
- In regular use, a rule outlined in an exterior fashion sheet which is overruled by a method outlined within the head of the doc, which in flip, is overruled by an inline fashion inside the aspect itself (assuming equal specificity of the selectors).
- Defining a rule with the !essential attribute that discards the traditional issues as regards the later rule overriding the sooner ones.
- So, it’s used for overriding the types which are beforehand declared in different fashion sources, with the intention to obtain a sure design.
Syntax:
aspect {
shade: blue !essential;
font-size: 14px !essential;
...
}
59. What’s specificity in CSS?
When a couple of set of CSS guidelines applies to the identical aspect, the browser must determine which particular set can be utilized to the aspect. The foundations the browser follows are collectively referred to as Specificity
Specificity Guidelines embrace:
- CSS fashion utilized by referencing exterior stylesheet has the bottom priority and is overridden by Inner and inline CSS.
- Inner CSS is overridden by inline CSS.
- Inline CSS has the very best precedence and overrides all different selectors.
Specificity Hierarchy: Each aspect selector has a place within the Hierarchy.
- Inline fashion: Inline fashion has the very best precedence.
- Identifiers(ID): ID has the second-highest precedence.
- Courses, pseudo-classes, and attributes: Courses, pseudo-classes, and attributes have come subsequent.
- Parts and pseudo-elements: Parts and pseudo-elements have the bottom precedence.
60. What are the attribute selectors?
The CSS Attribute Selector is used to pick a component with some particular attribute or attribute worth. It is a wonderful solution to fashion the HTML parts by grouping them based mostly on some particular attributes and the attribute selector will choose these parts with related attributes.
There are a number of sorts of attribute selectors that are mentioned under:
- [attribute] Selector: The sort of attribute selector is used to pick all the weather which have the desired attribute and applies the CSS property to that attribute. For instance, the selector [class] will choose all the weather with the fashion attribute.
- [attribute = “value”] Selector: This selector is used to pick all the weather whose attribute has the worth precisely the identical as the desired worth.
- [attribute~=”value”] Selector: This selector is used to pick all the weather whose attribute worth is an inventory of space-separated values, certainly one of which is strictly equal to the desired worth.
- [attribute|=”value”] Selector: This selector is used to pick all the weather whose attribute has a hyphen-separated record of values starting with the desired worth. The worth must be an entire phrase both alone or adopted by a hyphen.
- [attribute^=”value”] Selector: This selector is used to pick all the weather whose attribute worth begins with the desired worth. The worth doesn’t must be an entire phrase.
- [attribute$=”value”] Selector: This selector is used to pick all the weather whose attribute worth ends with the desired worth. The worth doesn’t must be an entire phrase.
- [attribute*=”value”] Selector: This selector selects all the weather whose attribute worth comprises the desired worth current anyplace. The worth doesn’t must be an entire phrase.







