Evaluation of ransomware traits in 2022 exhibits that enterprise was booming final 12 months for extortionary cybercriminals, with the very best quantity of ransomware assaults lobbed by subtle criminals that manage into teams that make the most of very constant techniques, methods, and procedures (TTPs) amongst themselves, even when these organizations “retire” after which come again, rebranded.
A Jan. 26 report from the Guidepoint Analysis and Intelligence Crew (GRIT) confirmed that whereas no less than one new ransomware group emerged each month final 12 months, nearly all of assaults had been perpetrated by a comparatively small group of entrenched gamers.
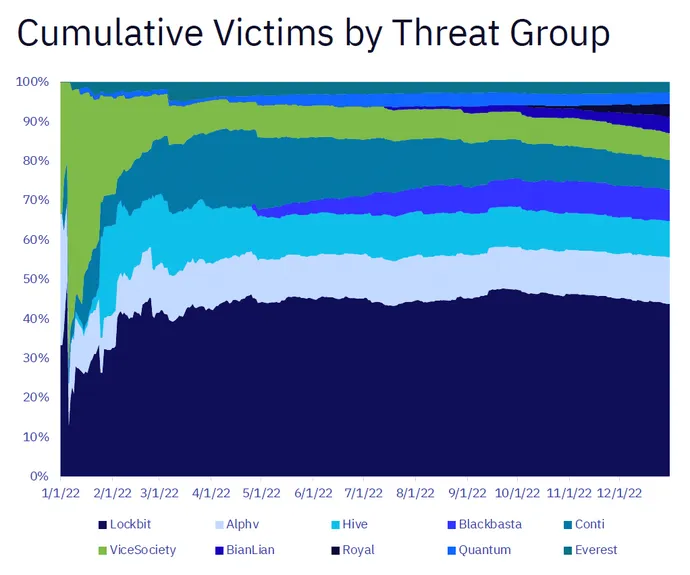
The “GRIT 2022 Ransomware Report” examined information and circumstances from 2,507 publicly posted ransomware victims throughout 40 business verticals that had been carried out by 54 lively menace teams.
“The factor that we actually wished to emphasise was that ransomware shouldn’t be going anyplace,” says Drew Schmitt, GRIT lead analyst and an skilled ransomware negotiator for GuidePoint Safety. “It’s totally current. Lots of people appear to suppose that ransomware is doubtlessly declining, due to issues like Bitcoin funds have gotten much less useful. However ransomware remains to be taking place at loopy charges.”
As a negotiator, Schmitt works with actively attacked firms to behave on their behalf and interface with the extortionist. There are two objectives: to both achieve sufficient data and time to assist their safety operations facilities (SOCs) get better, or to barter a decrease fee.
Utilizing his inside information about how attackers function, and the info freely accessible about victimology final 12 months, he and his crew had been capable of put collectively quite a few insights for the report. Darkish Studying caught up with Schmitt to not solely dig into particulars the report, but in addition to glean observations from his ongoing work as a negotiator. He offered seven key factors that defenders ought to remember as they put together for extra ransomware campaigns in 2023.
1. There is a Particular Taxonomy to Ransomware Gangs
An enormous a part of the evaluation revolved across the growth of a ransomware taxonomy for categorizing ransomware teams, which the crew organized into 4 buckets: full-time, rebrands, splinter, and ephemeral.
Nearly all of assaults got here from what the taxonomy dubbed full-time teams, which have been lively for 9 or extra months and publicly declare 10 or extra victims.
“These are the Lockbits of the world, and they’re those which might be doing very constant operations [and] can keep a really excessive tempo,” Schmitt says. “They’re very constant in behaviors and have lots of actually sturdy infrastructure. These are those which have been working for a really lengthy time period, they usually’re doing it constantly.”
Because the report identified, Lockbit alone accounted for 33% of assaults final 12 months.
Then there are the rebrand teams, which have been lively for lower than 9 months however declare almost the identical variety of victims as full-time teams, and with some examination of TTPs normally have some correlation with a retired group.
“Actually the one distinction between the rebrand and the fulltime is the period of operation,” Schmitt says. “Teams like Royal additionally match into this sort of class the place they only have very sturdy operations they usually’re capable of function at a excessive tempo.”
Meantime, “splinter” teams are people who have some TTP overlap with recognized teams, however are much less constant of their behaviors.
“The splinter teams are an offshoot from both a rebrand or a full-time, the place it is perhaps anyone going off and doing their very own factor,” he says. “They have not been round for very lengthy. Their identification shouldn’t be solidified at this cut-off date, they usually’re actually simply looking for themselves and the way they are going to function.”
Lastly rounding issues out are “ephemeral” teams which have been lively for lower than two months, which have assorted however low sufferer charges. Generally these teams come and go, whereas different instances they find yourself growing into extra mature teams.
2. Speedy Rebranding of Ransomware Teams Makes Risk Intelligence Key
The classification into these 4 taxonomy teams seems cleaner in an annual report than it does on the bottom when a SOC begins lighting up.
“Once you begin coping with these kind of teams which might be popping up and going away in a short time, or they’re rebranding, they’re growing new names, it does make it very far more troublesome for the blue teamers or the defenders to maintain up with these kind of traits,” says Schmitt, who explains that holding tabs on rebranding and splintering of teams is the place menace intelligence ought to come into play.
“We actually wish to deal with emphasizing communication relating to menace intelligence — whether or not it is menace intelligence speaking with the SOC or the incident response crew, and even vulnerability administration,” he says. “Getting an thought of what these traits appear to be, what the menace actors are specializing in, how a lot they pop up and go away, all of that could be very useful for the defenders to know.”
3. RaaS Teams Are a Wild Card in Negotiations
Although the underlying TTPs of fulltime teams makes lots of ransomware detection and response a bit simpler, there are nonetheless some huge variables on the market. For instance, as many teams have employed the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) mannequin, they make use of much more associates, which suggests negotiators are all the time coping with totally different folks.
“Within the early days of ransomware, once you began negotiations, there was a very good likelihood you had been coping with the identical particular person in case you had been coping with the identical ransomware,” Schmitt says. “However in in the present day’s ecosystem, there are simply so many alternative teams, and so many alternative associates which might be collaborating as a part of these teams, that lots of instances you are nearly ranging from scratch.”
4. Ransom Calls for Are Climbing Sky Excessive
One of many anecdotal observations Schmitt made was the truth that he is seen lots of very excessive preliminary ransom calls for from ransomware operators these days.
“We have seen $15 million, we have seen $13 million, we had $12.5 million. There’s lots of very excessive preliminary ransom calls for which have been taking place, which is a bit bit shocking,” he says. “And lots of instances we do efficiently negotiate considerably decrease ransoms. So beginning at $15 million and getting all the way down to $500,000 shouldn’t be unusual. However on the identical time there are simply sure menace actors which might be like, ‘You understand what? That is my worth and I do not care what you say, I am not going to barter.'”
5. Improved Backup Methods Are Making a Distinction in Preparation
The ratio of shoppers he sees who can efficiently get better with out caving to the extortion calls for versus people who have to pay a ransom is coming near a 1:1 parity, Schmitt says.
“Within the early days it was like, ‘Effectively crap, we received encrypted. We will not get better until we pay this ransom,'” he notes. “As time has gone on, having actually efficient backup methods has been large for having the ability to get better; there are lots of organizations that get hit with ransomware they usually’re capable of get better just because they’ve a extremely stable backup technique in place.”
6. Double Extortion Is the Norm
Nevertheless, there are nonetheless loads of organizations which might be nonetheless behind the curve, he says, which preserve ransomware extra worthwhile than ever. Moreover, the unhealthy guys are additionally adjusting by way of doubleextortion, not solely encrypting information, however stealing and threatening to publicly leak delicate data as nicely. The entire teams tracked within the report make the most of double extortion.
“It is a bit bit unclear whether or not that is simply because persons are getting higher at securitynor the teams are actually realizing that perhaps it is not definitely worth the effort to deploy the ransomware if the consumer already has a backup technique in place that is going to permit them to get better,” he says. “So, they have been specializing in that information exfiltration as a result of I believe they know that that is one of the best likelihood that they really should generate profits off of an assault.”
7. There’s No Honor Amongst Thieves, however There’s Enterprise Sense
Lastly, the large query in coping with legal extortionists is whether or not the unhealthy guys are even going to maintain their phrase as soon as the cash drops of their account. As a negotiator, Schmitt says that, for probably the most half, they usually achieve this.
“Clearly, there is not any honor amongst thieves, however they do consider of their repute,” he says. “There are edge instances the place one thing unhealthy occurs, however mostly the larger teams are going to verify they do not publish your information and they are going to present you the decryptor. It is not going to be some malware backdoor decryptor that is going to do extra injury. They’re very targeted on their repute, and their enterprise mannequin merely simply does not work in case you pay them after which they nonetheless leak your information or they do not offer you what they’re presupposed to.”


